
Photo Credit: by HeungSoon, from Pixabay
High blood sugar, commonly referred to as diabetes is one of the fastest growing medical conditions in our world today. There are two main types: The type 1 which is treated solely with insulin and the type 2 which can be treated by several medications. The choice of medication depends will vary from patient to patient depending on the presence or absence of other medical conditions.
Effective and safe medication is an absolute necessity in order to control symptoms of high blood sugar, reduce the risk of complications, and achieve good control of risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol and obesity.
While metformin is the first line treatment in conjunction with diet and exercise for type 2 diabetes, certain conditions and or factors like contraindications and or intolerances may make it inappropriate for a select group of patients. Metformin may also be combined with other classes of medication to improve clinical outcome in type 2 diabetic patients.
What are Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors?
SGLT2 inhibitors are a group of prescription medications that are recommended for use to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes as an adjunct to diet and exercise.
These group of medications work by preventing sugar reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to increased elimination of sugar in the urine thereby lowering blood sugar. Medications in this class includes canagliflozin (INVOKANA), dapagliflozin (FARXIGA), empagliflozin (JARDIANCE) and ertugliflozin (STEGALTRO). They are associated with weight loss, reduced blood pressure, and a lower risk of sudden drops of blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
These oral medications are available as single-ingredient products and in combination with other antidiabetic medications like metformin.
Side effects of note with this class of medications include fungal infections of the vagina and other infections of the female reproductive system, volume depletion-related adverse effects and some reports of diabetic ketoacidosis. Volume depletion related side effects is especially worse in patients taking diuretics (medications that remove fluids from the body).
Patients presenting with non-specific symptoms such as difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, anorexia, excessive thirst and unusual fatigue or sleepiness occur, regardless of blood glucose level should be immediately evaluated for Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). The medication must be discontinued immediately if DKA is diagnosed or suspected. SGLT 2 inhibitors are not recommended for use in patients with type 1 diabetes as safety and efficacy have not been proven.
What are the most commonly prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors?
The most commonly prescribed SGLT 2 inhibitors are Farxiga and Jardiance.
Farxiga is an SGLT2 inhibitor with dapagliflozin as its active ingredient. It was first approved for treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes as an adjunct to diet and exercise. It was later approved to reduce risk of hospitalization for heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes. More recently, it is now recommended for the treatment of heart failure in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and the treatment of chronic kidney disease in patients at risk of progression with or without type 2 diabetes.
It can be used as the sole medication for managing type 2 diabetes in patients who cannot take metformin for any reasons. It may also be combined with other medications such as metformin, glimepiride, gliclazide, sitagliptin (Jardiance) alone or with metformin insulin alone or with metformin. Farxiga is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to this drug or to any ingredient in the formulation and also patients on dialysis.
Dapaglifloxin is also marketed in Canada under the brand name Forxiga.
Jardiance is also an SGLT2 inhibitor with empagliflozin as its active ingredient. It was first approved for treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes. Later, it was approved to reduce cardiovascular death in adult patients with type 2 diabetes and to treat heart failure in adult patients with reduced ejection fraction. Most recently, it was approved for treatment of heart failure in adults.
Jardiance may be used alone to control blood sugar in patients that cannot use metformin for any reason. It may also be used in combination with other blood sugar lowering medications such metformin.
Over the years, some antidiabetic medications have been found to increase the risk of major cardiovascular events. However, Jardiance has been extensively studied and proven to reduce risk of major cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke. Farxiga does not worsen cardiovascular events either.
On the other hand, Farxiga is approved for treatment of chronic kidney disease. Research is still ongoing with Jardiance, many in clinical experts however believe this may also be the case for Jardiance.
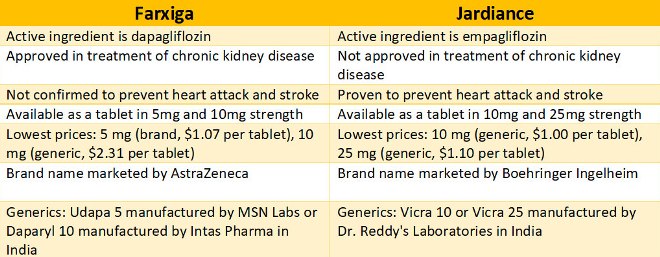
Photo Credit: by @CANPharmaWorld
In conclusion, it is obvious that both Farxiga and Jardiance belong to the same class of medication which confers similar benefits and side effect profile across board in treatment of type 2 diabetes. How to determine which drug is best for you? Your doctor will perform a comprehensive review of your medical conditions. For example, the presence of other medical conditions such as heart disease, heart failure or chronic kidney disease will determine which of the 2 medications will be prescribed for you by your doctor.
###
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *.